After the recent Nigerian election, the country found itself with a new President, Ahmed Tinubu. However, he is inheriting a frail economy with record levels of debt and excessive levels of inflation alongside worrying shortages of foreign exchange reserves[i], weakening oil production, a weakening currency, and a declining power supply.
Despite this, he vowed during his inauguration ceremony to expand the Nigerian economy by a minimum of 6% per year, unify the foreign exchange rate, remove costly fuel subsidies, and tackle extensive insecurity, contrasting with his predecessor Buhari who deployed a series of protectionist policies[ii] which spooked international investors.
What are his plans for the Nigerian Economy?
Remove fuel subsidies
According to the President of the African Development Bank, Dr Akinwunmi Adesina, the "fuel subsidy benefits the rich and kills Nigeria’s economy" due to the rampant fraud we have seen take place over recent years. The removal of the subsidy would help to save enormous amounts of money for the government, which can then be used to address a plethora of issues faced currently by Nigeria and help Tinubu achieve his plans for the economy.
Infrastructure provision
This has the potential to improve the economy in multiple ways as it provides physical assets and jobs. Supplying electricity has been said to be a priority of the new administration and generation, transmission and distribution are to be doubled and state governments will be encouraged to participate in assisting with the plans.
This is expected to encourage foreign investment in Nigeria, which is currently low, and we can even see that Nigerians invest more externally than inside Nigeria. However, with adequate provision of labour, which can certainly be achieved as Nigeria has more young citizens than older, and friendly investment policies, Nigeria can become attractive to foreign investors.
Increased foreign investment has a multitude of benefits. Firstly, it is likely to increase employment, giving consumers more income, which may then lead to a positive multiplier effect[iii] as this increased income is spent multiple times in the economy, improving economic growth. This effect could also be further enhanced by the promised tax cuts for poor income earners. On the other hand, this effect could be reduced if people choose to save their increased income rather than spend it, which could be likely due to the current state of the Nigerian economy leading to many having low confidence.
Bank interest rates
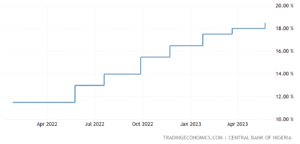
Source: Trading Economics
Many believe that the interest rates of banks are too high and discourage business investment. The President has now assured that the government will look for ways to lower the interest rate, which would likely encourage investment from businesses as loans become more accessible for more firms and individuals. A lower interest rate would reduce the cost of borrowing, making many more likely to take the risk associated with a loan. The increased amount of investment this may lead to is likely to benefit the economy for multiple reasons. If people are spending more in the economy, then it is likely to both increase business profits and increase the derived demand for labour, causing an increase in employment. This would likely improve business confidence and, as such, promote further investment from businesses, possibly into Research and Development, improving dynamic efficiency[iv], perhaps causing further business growth and likely leading to economic growth benefitting the entire country, especially as it would lead to increased government revenue which could then be reinvested into the economy.
What does the future hold for Nigeria’s economy?
While these plans could be said to be a great start, we are still in the early stages of Tinubu’s term as President, so we will need to wait much longer to see if his policies have their intended effects and, while they certainly have potential, it is debatable whether it is enough to truly fix Nigeria’s long-standing issues especially considering the country’s history with corruption and funds not reaching their intended destinations. Nonetheless, these policies are undoubtedly welcome as Nigeria looks to tackle the concerns it currently faces, which won’t happen without action being taken.
Footnotes:
[i] Foreign Exchange Reserves - Assets held on reserve by a central bank in foreign currencies.
[ii] Protectionist Policies - The policies of protecting domestic industries against foreign competition through tariffs, import quotas and subsidies, or other restrictions placed on the imports of foreign competitors.
[iii] Positive Multiplier Effect - When an initial injection into the circular flow of income leads to a more than proportionate growth in national income.
[iv] Dynamic Efficiency - Dynamic efficiency is concerned with the productive efficiency of a firm over a period of time.
Bibliography:
Implications of key economic policies of current administration - Punch